Set接口和List接口一样,继承Collection接口,Set接口中元素无序,并且都会以某种规则保证存入的元素不出现重复。
HashSet是Set接口的一个实现类,所存储的元素是不可重复的,并且元素都是无序的,当向HashSet集合中添加一个对象时,首先会调用该对象的hashCode()方法来计算对象的哈希值,从而确定元素的存储位置。如果此时哈希值相同,再调用对象的equals()方法来确保该位置没有重复元素。
package 集合类;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Set {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set=new HashSet();
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
set.add("abc");
set.add("hello");
Iterator it=set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object obj=it.next();
System.out.print(obj+ " ");
}
}
}运行结果
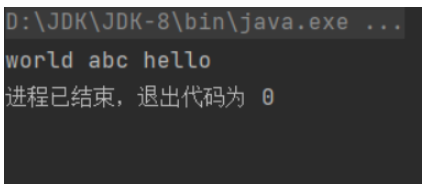
由运行结果可以看出,取出元素的顺序和添加元素的顺序并不一致,并且重复的字符串被去掉了,只添加了一次,是因为HashSet集合的add()方法存入元素时,首先调用当前存入对象的hashCode()方法获得对象的哈希值,然后根据哈希值算出一个存储位置,如果这个位置上没有元素,则直接将该元素存入,如果该位置上有元素存在,则会调用equal()方法让当前存入的元素依次和该位置上的元素比较。如果返回结果为false就将该元素存入集合,返回结果为true,则说明有重复元素,将该元素舍弃。
package 集合类;
import java.util.HashSet;
class Student{
String id;
String name;
public Student(String id,String name){
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
}
public String toString(){
String s = id + ":" + name;
return s;
}
}
public class Set1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hs=new HashSet();
Student stu1=new Student("1","hello");
Student stu2=new Student("2","world");
Student stu3=new Student("1","hello");
hs.add(stu1);
hs.add(stu2);
hs.add(stu3);
System.out.println(hs);
}
}运行结果
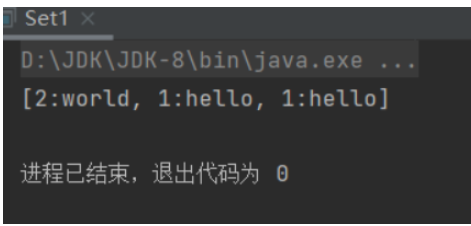
所没有去掉重复的元素,是因为在定义Student类时没有重写hashCode()和equals()方法。
package API;
import java.util.HashSet;
class Student{
private String id;
private String name;
public Student(String id,String name){
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
}
//重写toString方法
public String toString(){
return id+ ":"+name;
}
//重写hashCode方法
public int hashCode(){
//返回id属性的哈希值
return id.hashCode();
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
//判断是否是同一个对象
if(this==obj){
return true;
}
//判断对象是Student类型
if(!(obj instanceof Student)){
return false;
}
//将对象强转为Student类型
Student stu=(Student) obj;
//判断id是否相同
boolean b=this.id.equals(stu.id);
return b;
}
}
public class Set2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hs=new HashSet();
Student stu1=new Student("1","hello");
Student stu2=new Student("2","world");
Student stu3=new Student("1","hello");
hs.add(stu1);
hs.add(stu2);
hs.add(stu3);
System.out.println(hs);
}
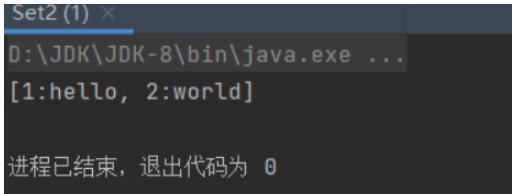
}运行结果
由于Student类重写了Object类的hashCode()和equals()方法。在hashCode()方法中返回id属性的哈希值,在equals()方法中比较对象的id属性是否相等,并返回结果。当调用HashSet集合的add()方法添加stu3对象时,发现它的哈希值与stu2对象相同,而且stu2.equals(stu3)返回true。HashSet认定两个对象相同,因此重复的Student对象被去除了。